Conveyor belts find widespread application in various industries, such as logistics, mining, agriculture, and manufacturing, enabling the seamless movement of goods over short or long distances. Their design and functionality can be customised to accommodate diverse requirements, making them indispensable in streamlining production workflows and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Enhance your Warehouse with Conveyor Systems
From assembly lines to baggage handling at airports, conveyor belts play a pivotal role in facilitating the smooth flow of materials, contributing significantly to the advancement of modern industrial processes. Find out more about conveyor belts below and start enhancing your warehouse with Conveyor Systems Ltd today.
How Are Conveyor Belts Made?
Conveyor belts serve diverse purposes across industries, with varying designs tailored to specific needs. In warehouses, they feature a pre-punched, mild steel folded framework and supports with powder coat paint for durability. In sectors like pharmaceuticals and food and beverages, stainless-steel frameworks and supports ensure cleanliness.
Terminal rollers at both ends of the conveyor belt reduce friction, and the belt, cut to length, runs on a smooth steel bed or conveyor rollers for heavier loads. By joining the two ends of the belt, endless assembly can be utilised.
Tensioning devices are used to prevent slipping due to the belt stretching over time. Drive mechanisms, either an integral drive motor or a separate drive, are used to facilitate belt movement which can offer versatility for reversible conveyor belts.
Designing Your Conveyor Belt
Conveyor belt designs vary significantly based on the handled product. Generally, a predominantly flat base is utilised to prevent product displacement.
For products intended for human consumption, like pharmaceuticals or food, the design prioritises easy cleanability and is devoid of dirt traps. Factors such as product weight, dimensions, and fragility dictate the conveyor belt’s size and type, ensuring adaptability to diverse items. Additionally, the maximum product weight determines the motor/gearbox size for optimal belt movement.
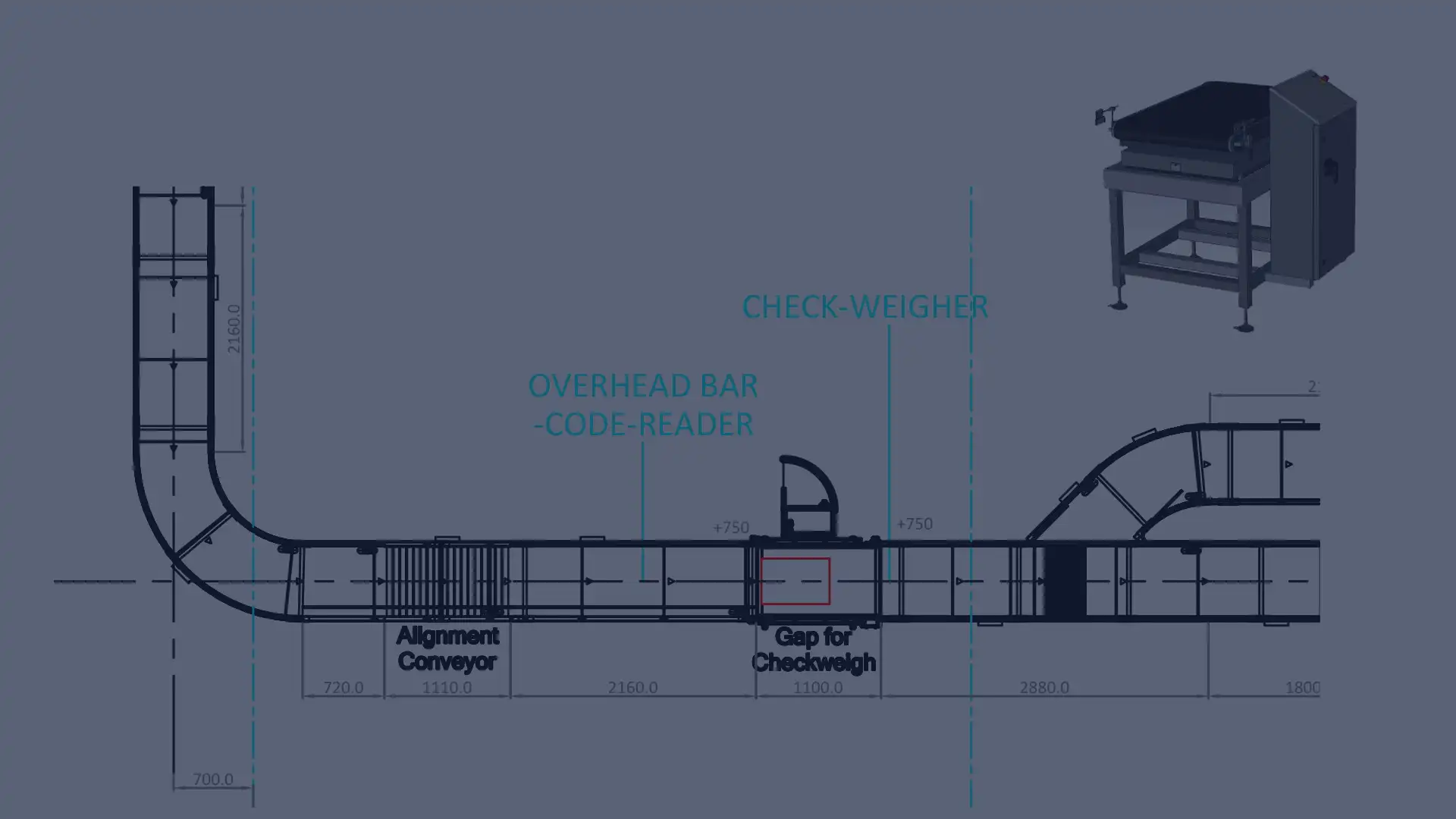
Conveyor belts may need to facilitate automatic sorting for destinations, requiring gaps and alignment for barcode readers. Furthermore, conveyor belts may not always be horizontal, adapting to processes that require inclined transportation for elevated destinations.
If you require a conveyor belt system, our team at Conveyor Systems is on hand to find the solution for you. Contact us today to elevate your warehouse and enhance your efficiency.
Calculating Conveyor Belt Length
After determining the conveyor belt frame length for efficient product movement in a warehouse, the belting length must be calculated. The laid-out belting, initially matching the frame length “X,” completes an endless loop by returning under the frame, resulting in a doubled length (2″X”).
To prevent the belt from slipping over time due to stretching, a tensioning unit is crucial at the frame’s end drum roller. This unit, equipped with adjustable long bolts, ensures the end roller compensates for any slack. The final design length factors in stretch considerations, which is influenced by conveyor dimensions, weight capacity, and stop/start frequency as a percentage of the overall belt conveyor length.
Calculating Conveyor Belt Capacity
The capacity of a conveyor belt depends on the design, dimensions, and type of product being transported on the conveyor belt. A conveyor system is capable of transporting numerous small, lightweight items like padded envelopes, whereas heavier parcels such as fully loaded tote bins necessitate a different design.
Design considerations, such as the product type and peak weight on the conveyor belt, are vital for determining its capacity. The conveyor belt width is determined by the maximum product dimensions, with wider belts carrying less weight over the same distance. Continuous loading enables greater volume conveyance compared to systems with frequent stop/starts.
Calculating Conveyor Belt Horsepower
The horsepower requirement to drive a conveyor belt depends on a number of factors such as conveyor length, width and weight to be carried. If the horsepower selected is too small for the weight on the conveyor, it could overload the 3-phase motor on the conveyor belt and cause it to stop running. Conversely, if the conveyor belt has a 3-phase motor too large for the requirement it will be a waste of energy usage.
The number of conveyor belt stop/starts per hour will affect the horsepower calculations as the slower the speed, the higher the torque which means the motor/gearbox has to work harder. This means the design calculation will show more power is required.
If the motor/gearbox on the conveyor belt is designed to run at a variable speed to suit a manufacturing process or to run at high speeds, the horsepower calculation will need to reflect this. Additionally, belt conveyors can also be driven by 24-volt driven rollers which have an integral motor encased within the roller, but horsepower is calculated in the same way.
Conveyor Belt Fabrication
The conveyor belt fabrication process significantly influences the capabilities, durability, and overall performance of the entire system. Diverse manufacturing approaches are employed by conveyor belt manufacturers, with thermoplastic manufacturers utilising injection molding or extrusion to craft modular components that are assembled into complete conveyor belts with pre-manufactured drive systems.
What material are conveyor belts made of?
Conveyor belts feature a range of materials, including nylon, polyester, rubber, mild and stainless steel, and thermoplastics. The material’s characteristics and strength play a pivotal role in determining the conveyor system’s applications.
General handling applications, like those in eCommerce and manufacturing, may favour polyester or other fabric belts for flexibility. Conversely, industries such as food, beverage, and pharmaceuticals demand food-grade materials like thermoplastics and stainless steel.
How does this apply to my industry?
Various conveyor belts integrate an inner core layer for strength, with fabric, plastic, or rubber surfaces covering the top and bottom to suit handled products. In sectors like food packing, inclined food-grade conveyor belts with cleats or trough shaping facilitate the seamless transfer of bulk produce into high-level weighing and packaging machines.
The pharmaceutical industry relies on thermoplastic and stainless-steel conveyor belts to meet stringent sterility requirements in lab and production settings. For chemical manufacturers dealing with corrosives and high temperatures, conveyor belts made of thermoplastics, rubber, or steel with special coatings are essential to withstand these challenges.
Steel belts with small perforations provide a vacuum hold for delicate items, while woven, hinged, and custom belts handle small electronics, foods, and various production line components. Stainless steel and aluminium conveyor belts can incorporate coatings like Teflon or neoprene based on friction requirements. Overall, the conveyor belt fabrication process is a critical determinant of its suitability for specific industrial applications.
Conveyor Belt Installation
There are several factors to consider well before a conveyor belt system is installed in any eCommerce fulfilment centre, warehouse, distribution centre, manufacturing facility or assembly plant. There are many considerations such as the location, size of installation and convenience for the customer that can influence how your conveyor belt is installed.
Installation into a Fully Operational Facility
In the event that the new conveyor system is to be installed in a fully operational facility, it is imperative to ensure the least disruption to the ongoing business. Procedures that meet current Health and Safety guidelines also need to be considered meaning a full site survey by Project Engineers must be carried out well in advance to check provisions for delivery, access, ingress, power supply position and confirm pre-agreed timescales with the customer.
Installation into a New Building
If a conveyor belt system is to be installed in a brand-new building, additional considerations have to be given to the presence of other contractors, lack of lighting/power supply, amenities, and additional H.S.E. considerations.
Large Conveyor Belt System Installation
On larger conveyor belt installations, delivery and installation of the equipment will have to be phased to avoid causing issues for both the customer and making it harder for the installation engineers to find/access the appropriate parts in the correct order.
The Conveyor System Installation Process
1. Delivering the Components and Assembly
Generally, the equipment is delivered already partially assembled in set lengths on pallets. Once these conveyor mechanical parts have started to be installed, the control engineers can begin fitting all the electrical items such as cabling, electrical devices, and control panels.
2. Software Uploads
Once all mechanical and electrical work is complete, the pre-written software can be loaded into the panel-based PLC/PC (system controller) to integrate all the information. Conveyor belt control processes are also uploaded. This creates a total working system to integrate and work with a wider warehouse/production automation solution.
3. Final Checks and Customer Training
After all the motors on the conveyor belts have power, the commissioning phase starts. This allows the engineers to ensure the conveyor belts perform the correct function they were designed for and that the products are handled without issues to the customer’s satisfaction. At the same time, customer personnel training is carried out on how to operate, fault find, and maintain the conveyor belt system.
How Much Does a Conveyor Belt Cost?
There are several costs to consider when purchasing a conveyor belt system. This includes the cost of the conveyor belt hardware, controls, and installation.
The initial purchase cost of any conveyor belt system includes:
- The cost of painted or stainless-steel framework
- Precision end terminal rollers
- Conveyor belting
- Drive motor/gearbox
- Labour cost to assemble the conveyor belt
The conveyor belt cost will also include a charge for the bespoke control panel and software which will be sized to suit the extent of the conveyor belt system and number of drives along with all the electrical panel and components to control the operation of the conveyor belts.
Additionally, operational costs should be considered such as electrical usage and air consumption via a compressor. Conveyor belt maintenance budgeting must also be considered, such as:
- The cost of stocking critical spare parts
- Breakdown replacement parts
- In-house labour costs for its upkeep
- The cost of a service contract with the manufacturer
All of these costs can vary widely due to the various sizes, materials, and duties which are tailored to the customer’s specific needs. If you want to elevate your warehouse today, get in touch with us and we will find the solution for you.
Enhance Your Warehouse With Conveyor Systems Ltd
At Conveyor Systems, we have a team of experts ready to find the answers to your warehouse challenges. Whether you need traditional conveyor belts, automated sortation conveyor systems, vertical storage systems, vertical lift conveyor systems or autonomous mobile robots to enhance your warehouse or fulfillment centre, our team can provide you with tailored solutions that meet your needs.
We also offer a range of maintenance services from mechanical servicing to breakdown maintenance to spare parts. If you want to start building your perfect warehouse or fulfillment center today, contact us and one of our experts will assist you.